LA BIBLIO DU MOIS: Février 2021
LA BIBLIO DU MOIS: Février 2021
Encore plein d’articles intéressants ce mois-ci !
Bien sûr un peu de COVID-19 au cas où vous auriez un petit goût de pas assez, notamment des essais prometteurs sur des nouveaux candidats pour la création de nouveaux vaccins, mais aussi l’intérêt de certaines molécules comme la dexaméthasone.
Du côté de la réanimation, retour sur la dysfonction ventriculaire droite dans le choc septique, ou encore sur la PCT & l’éternel débat sur sa spécificité pour détecter une infection bactérienne, focus sur l’évolution psychiatrique des patients ayant présenté un épisode délirant durant leur hospitalisation, et encore plein d’autres sujets passionnants !!
Bon courage à tous pour les semaines à venir qui s’annoncent intenses pour notre spécialité !
LES INDÉTRÔNABLES :
✦ Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19
Référence / DOI : 10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Résumé article :
COVID-19 est associée à une atteinte pulmonaire diffuse. Les glucocorticoïdes pourraient moduler l’inflammation responsable de l’agression pulmonaire et donc réduire la progression vers la défaillance respiratoire et la mort.
Etude contrôlée, ouverte, comparant les traitements possibles des patients hospitalisés pour le covid 19, randomisation pour recevoir de la dexamethasone (DXM) par voie orale ou intraveineuse pour une durée de 10 jours versus une prise en charge standard. Critère de jugement principal à 28 jours est la mortalité.
Résultats :
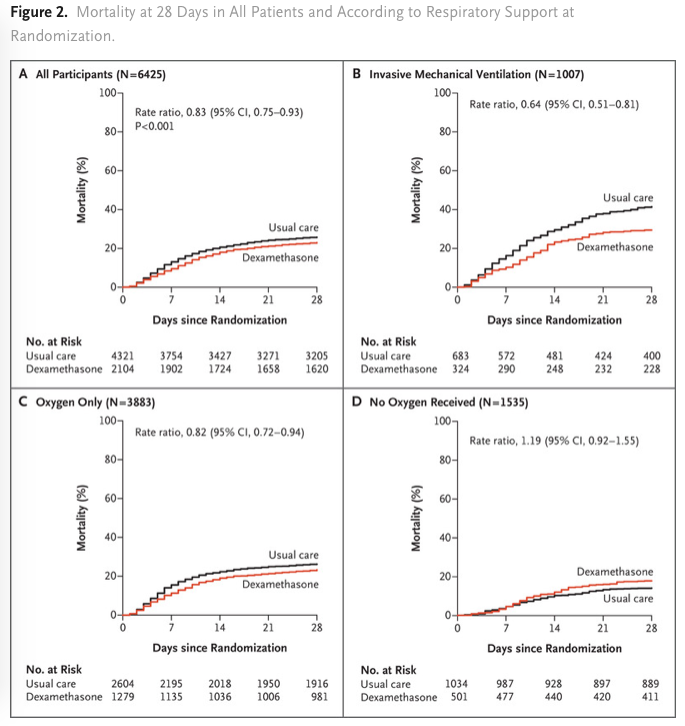
Total de 2104 patients ont été assignés pour reçevoir de la DXM et 4321 patients ont reçu des soins standards. 482 patients (22,9%) des patients du groupe DXM et 1110 patients (25,7%) du groupe soins standards sont décédés à 28 jours de la randomisation (significatif après ajustement sur l’âge). La proportion et la différence absolue de mortalité varient considérablement selon le niveau de support respiratoire reçus par les patients lors de la randomisation. Dans le groupe DXM, l’incidence de la mortalité était significativement plus faible (29,3%) que dans le groupe standard (41,4%) parmi les patients sous ventilation mécanique invasive et dans le groupe des patients recevant de l’oxygène sans ventilation mécanique invasive (23.3% vs. 26.2%; rate ratio, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.72 to 0.94) mais pas au sein des patients ne recevant aucun support respiratoire ((17.8% vs. 14.0%; rate ratio, 1.19; 95% CI, 0.92 to 1.55).
Conclusions L’utilisation de la DXM dans le covid 19 diminue la mortalité à J-28 parmi les patients recevant une ventilation mécanique invasive ou de l’oxygène seule lors de la randomisation mais pas chez ceux qui ne recevaient aucun support respiratoire.
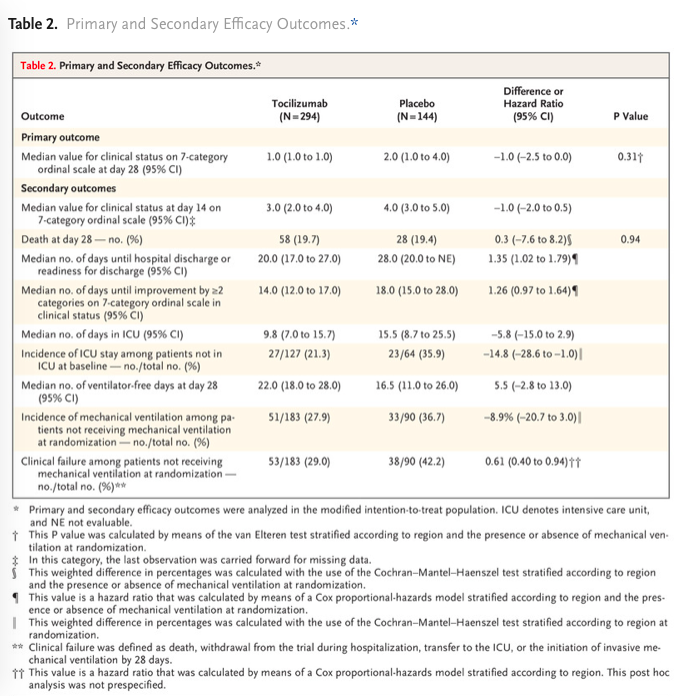
✦ Tocilizumab in Hospitalized Patients with Severe Covid-19 Pneumonia
Référence / DOI : 10.1056/NEJMoa2028700
Résumé article :
Abstract La covid 19 est associée à une dérégulation immunitaire et une hyperinflammation comprenant des taux élevé d’IL-6. L’utilisation du Tocilizumab un anticorps anti-Récepteur de l’IL6 permettrait-elle d’améliorer le pronostic des patients ayant une pneumonie covid sévère ?
Etude de phase 3 comparant les patients hospitalisés pour une pneumonie sars cov2 sévère recevant une injection iv unique de tocilizumab(8 mg/kg) à un groupe placebo. Le critère de jugement principal était le statut clinique à J28 sur une échelle ordinale entre 1 (sortant de l’hôpital) et 7 (le décès) dans une analyse en intention de traiter qui comparait la population ayant reçu au moins une dose de Tocilizumab versus placebo.
Résultats non significatifs sur le critère de jugement principal. Mortalité à J28 non différente entre le groupe tocilizumab et placebo.
✦ Terlipressin plus Albumin for the Treatment of Type 1 Hepatorenal Syndrome
Référence / DOI : 10.1056/NEJMoa2008290
Article avec beaucoup de biais, beaucoup de choses à discuter 5* pour une biblio.
Résumé article :
La terlipressine est utilisée dans le syndrome hépato rénal de type 1 dans de nombreux pays du monde et fait partie des recommandations en Europe.
Etude de phase 3 visant à confirmer l’efficacité et la sécurité de la terlipressine + albumine chez les adultes ayant un Sd hepato-rénal (SHR) de type 1. Randomisation Terlipressine vs placebo durant 14 jours. Le critère de jugement principal était la réversibilité du syndrome hépatorénal 10 jours après la fin du traitement.
Au total 300 patients inclus et randomisés, significativement plus de réversibilité du SHR dans le groupe terlipresssine, mortalité à J90 plus importante dans le groupe de terlipressine en raisons des complications respiratoires.
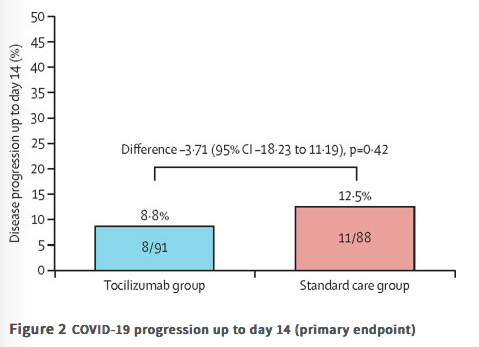
✦ Tocilizumab plus standard care versus standard care in patients in India with moderate to severe COVID-19-associated cytokine release syndrome (COVINTOC): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial
Référence : DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00081-3
Résumé article :
Background Global randomised controlled trials of the anti-IL-6 receptor antibody tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 have shown conflicting results but potential decreases in time to discharge and burden on intensive care. Tocilizumab reduced progression to mechanical ventilation and death in a trial population enriched for racial and ethnic minorities. We aimed to investigate whether tocilizumab treatment could prevent COVID-19 progression in the first multicentre randomised controlled trial of tocilizumab done entirely in a lower-middle-income country.
Methods COVINTOC is an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial done at 12 public and private hospitals across India. Adults (aged ≥18 years) admitted to hospital with moderate to severe COVID-19 (Indian Ministry of Health grading) confirmed by positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR result were randomly assigned (1:1 block randomisation) to receive tocilizumab 6 mg/kg plus standard care (the tocilizumab group) or standard care alone (the standard care group). The primary endpoint was progression of COVID-19 (from moderate to severe or from severe to death) up to day 14 in the modified intention-to-treat population of all participants who had at least one post-baseline assessment for the primary endpoint. Safety was assessed in all randomly assigned patients. The trial is completed and registered with the Clinical Trials Registry India (CTRI/2020/05/025369).
Findings 180 patients were recruited between May 30, 2020, and Aug 31, 2020, and randomly assigned to the tocilizumab group (n=90) or the standard care group (n=90). One patient randomly assigned to the standard care group inadvertently received tocilizumab at baseline and was included in the tocilizumab group for all analyses. One patient randomly assigned to the standard care group withdrew consent after the baseline visit and did not receive any study medication and was not included in the modified intention-to-treat population but was still included in safety analyses. 75 (82%) of 91 in the tocilizumab group and 68 (76%) of 89 in the standard care group completed 28 days of follow-up. Progression of COVID-19 up to day 14 occurred in eight (9%) of 91 patients in the tocilizumab group and 11 (13%) of 88 in the standard care group (difference −3·71 [95% CI −18·23 to 11·19]; p=0·42). 33 (36%) of 91 patients in the tocilizumab group and 22 (25%) of 89 patients in the standard care group had adverse events; 18 (20%) and 15 (17%) had serious adverse events. The most common adverse event was acute respiratory distress syndrome, reported in seven (8%) patients in each group. Grade 3 adverse events were reported in two (2%) patients in the tocilizumab group and five (6%) patients in the standard care group. There were no grade 4 adverse events. Serious adverse events were reported in 18 (20%) patients in the tocilizumab group and 15 (17%) in the standard care group; 13 (14%) and 15 (17%) patients died during the study.
Interpretation Routine use of tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with moderate to severe COVID-19 is not supported. However, post-hoc evidence from this study suggests tocilizumab might still be effective in patients with severe COVID-19 and so should be investigated further in future studies.
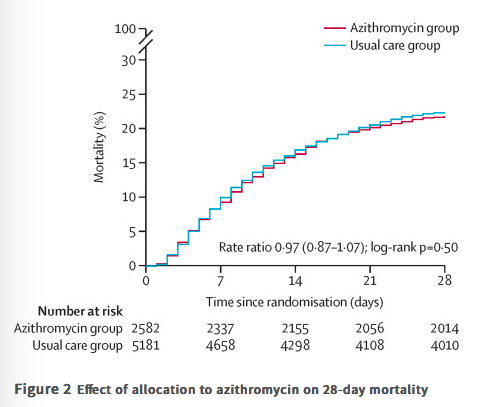
✦ Azithromycin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label platform trial
Référence : DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00149-5
L’azithromycine, connu pour ses propriétés immuomodulatrices, était potentiellement un bon candidat pour améliorer la prise en charge des patients atteints de COVID-19, mais en pratique qu’est-ce-que ça donne ?
Résumé article :
Background Azithromycin has been proposed as a treatment for COVID-19 on the basis of its immunomodulatory actions. We aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of azithromycin in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19.
Methods In this randomised, controlled, open-label, adaptive platform trial (Randomised Evaluation of COVID-19 Therapy [RECOVERY]), several possible treatments were compared with usual care in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 in the UK. The trial is underway at 176 hospitals in the UK. Eligible and consenting patients were randomly allocated to either usual standard of care alone or usual standard of care plus azithromycin 500 mg once per day by mouth or intravenously for 10 days or until discharge (or allocation to one of the other RECOVERY treatment groups). Patients were assigned via web-based simple (unstratified) randomisation with allocation concealment and were twice as likely to be randomly assigned to usual care than to any of the active treatment groups. Participants and local study staff were not masked to the allocated treatment, but all others involved in the trial were masked to the outcome data during the trial. The primary outcome was 28-day all-cause mortality, assessed in the intention-to-treat population.
Findings Between April 7 and Nov 27, 2020, of 16 442 patients enrolled in the RECOVERY trial, 9433 (57%) were eligible and 7763 were included in the assessment of azithromycin. The mean age of these study participants was 65·3 years (SD 15·7) and approximately a third were women (2944 [38%] of 7763). 2582 patients were randomly allocated to receive azithromycin and 5181 patients were randomly allocated to usual care alone. Overall, 561 (22%) patients allocated to azithromycin and 1162 (22%) patients allocated to usual care died within 28 days (rate ratio 0·97, 95% CI 0·87–1·07; p=0·50). No significant difference was seen in duration of hospital stay (median 10 days [IQR 5 to >28] vs 11 days [5 to >28]) or the proportion of patients discharged from hospital alive within 28 days (rate ratio 1·04, 95% CI 0·98–1·10; p=0·19). Among those not on invasive mechanical ventilation at baseline, no significant difference was seen in the proportion meeting the composite endpoint of invasive mechanical ventilation or death (risk ratio 0·95, 95% CI 0·87–1·03; p=0·24).
Interpretation In patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19, azithromycin did not improve survival or other prespecified clinical outcomes. Azithromycin use in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 should be restricted to patients in whom there is a clear antimicrobial indication.
✦ Safety and immunogenicity of S-Trimer (SCB-2019), a protein subunit vaccine candidate for COVID-19 in healthy adults: a phase 1, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Référence : https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)00241-5/fulltext
Essai de phase 1 d’un vaccin prometteur en cours de développement !
Résumé article :
Background As part of the accelerated development of vaccines against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), we report a dose-finding and adjuvant justification study of SCB-2019, a protein subunit vaccine candidate containing a stabilised trimeric form of the spike (S)-protein (S-Trimer) combined with two different adjuvants.
Methods Our study is a phase 1, randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial at a specialised clinical trials centre in Australia. We enrolled healthy adult volunteers in two age groups: younger adults (aged 18–54 years) and older adults (aged 55–75 years). Participants were randomly allocated either vaccine or placebo using a list prepared by the study funder. Participants were to receive two doses of SCB-2019 (either 3 μg, 9 μg, or 30 μg) or a placebo (0·9% NaCl) 21 days apart. SCB-2019 either had no adjuvant (S-Trimer protein alone) or was adjuvanted with AS03 or CpG/Alum. The assigned treatment was administered in opaque syringes to maintain masking of assignments. Reactogenicity was assessed for 7 days after each vaccination. Humoral responses were measured as SCB-2019 binding IgG antibodies and ACE2-competitive blocking IgG antibodies by ELISA and as neutralising antibodies by wild-type SARS-CoV-2 microneutralisation assay. Cellular responses to pooled S-protein peptides were measured by flow-cytometric intracellular cytokine staining.
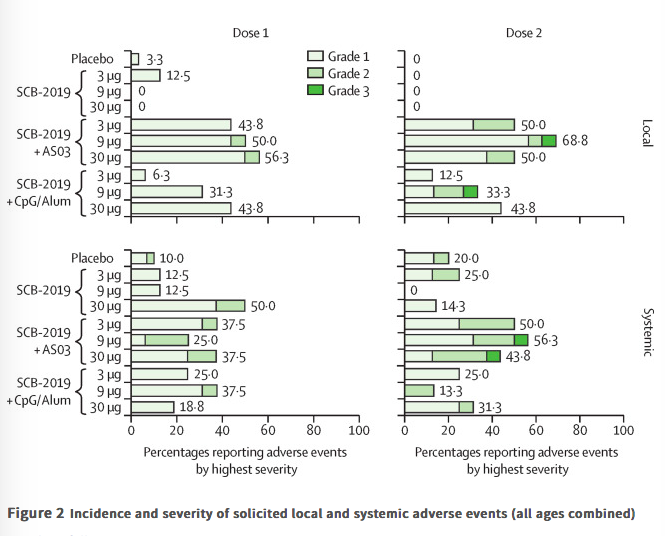
Findings Between June 19 and Sept 23, 2020, 151 volunteers were enrolled; three people withdrew, two for personal reasons and one with an unrelated serious adverse event (pituitary adenoma). 148 participants had at least 4 weeks of follow-up after dose two and were included in this analysis (database lock, Oct 23, 2020). Vaccination was well tolerated, with two grade 3 solicited adverse events (pain in 9 μg AS03-adjuvanted and 9 μg CpG/Alum-adjuvanted groups). Most local adverse events were mild injection-site pain, and local events were more frequent with SCB-2019 formulations containing AS03 adjuvant (44–69%) than with those containing CpG/Alum adjuvant (6–44%) or no adjuvant (3–13%). Systemic adverse events were more frequent in younger adults (38%) than in older adults (17%) after the first dose but increased to similar levels in both age groups after the second dose (30% in older and 34% in younger adults). SCB-2019 with no adjuvant elicited minimal immune responses (three seroconversions by day 50), but SCB-2019 with fixed doses of either AS03 or CpG/Alum adjuvants induced high titres and seroconversion rates of binding and neutralising antibodies in both younger and older adults (anti-SCB-2019 IgG antibody geometric mean titres at day 36 were 1567–4452 with AS03 and 174–2440 with CpG/Alum). Titres in all AS03 dose groups and the CpG/Alum 30 μg group were higher than were those recorded in a panel of convalescent serum samples from patients with COVID-19. Both adjuvanted SCB-2019 formulations elicited T-helper-1-biased CD4+ T-cell responses.
Interpretation The SCB-2019 vaccine, comprising S-Trimer protein formulated with either AS03 or CpG/Alum adjuvants, elicited robust humoral and cellular immune responses against SARS-CoV-2, with high viral neutralising activity. Both adjuvanted vaccine formulations were well tolerated and are suitable for further clinical development.
✦ Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18-59 years: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase ½ clinical trial.
Référence : https://www.thelancet.com/journals/laninf/article/PIIS1473-3099(20)30843-4/fulltext
Résumé article :
Background With the unprecedented morbidity and mortality associated with the COVID-19 pandemic, a vaccine against COVID-19 is urgently needed. We investigated CoronaVac (Sinovac Life Sciences, Beijing, China), an inactivated vaccine candidate against COVID-19, containing inactivated severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), for its safety, tolerability and immunogenicity.
Methods In this randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial, healthy adults aged 18–59 years were recruited from the community in Suining County of Jiangsu province, China. Adults with SARS-CoV-2 exposure or infection history, with axillary temperature above 37·0°C, or an allergic reaction to any vaccine component were excluded. The experimental vaccine for the phase 1 trial was manufactured using a cell factory process (CellSTACK Cell Culture Chamber 10, Corning, Wujiang, China), whereas those for the phase 2 trial were produced through a bioreactor process (ReadyToProcess WAVE 25, GE, Umea, Sweden). The phase 1 trial was done in a dose-escalating manner. At screening, participants were initially separated (1:1), with no specific randomisation, into two vaccination schedule cohorts, the days 0 and 14 vaccination cohort and the days 0 and 28 vaccination cohort, and within each cohort the first 36 participants were assigned to block 1 (low dose CoronaVac [3 μg per 0·5 mL of aluminium hydroxide diluent per dose) then another 36 were assigned to block 2 (high-dose Coronavc [6 μg per 0·5 mL of aluminium hydroxide diluent per dse]). Within each block, participants were randomly assigned (2:1), using block randomisation with a block size of six, to either two doses of CoronaVac or two doses of placebo. In the phase 2 trial, at screening, participants were initially separated (1:1), with no specific randomisation, into the days 0 and 14 vaccination cohort and the days 0 and 28 vaccination cohort, and participants were randomly assigned (2:2:1), using block randomisation with a block size of five, to receive two doses of either low-dose CoronaVac, high-dose CoronaVac, or placebo. Participants, investigators, and laboratory staff were masked to treatment allocation. The primary safety endpoint was adverse reactions within 28 days after injection in all participants who were given at least one dose of study drug (safety population). The primary immunogenic outcome was seroconversion rates of neutralising antibodies to live SARS-CoV-2 at day 14 after the last dose in the days 0 and 14 cohort, and at day 28 after the last dose in the days 0 and 28 cohort in participants who completed their allocated two-dose vaccination schedule (per-protocol population).
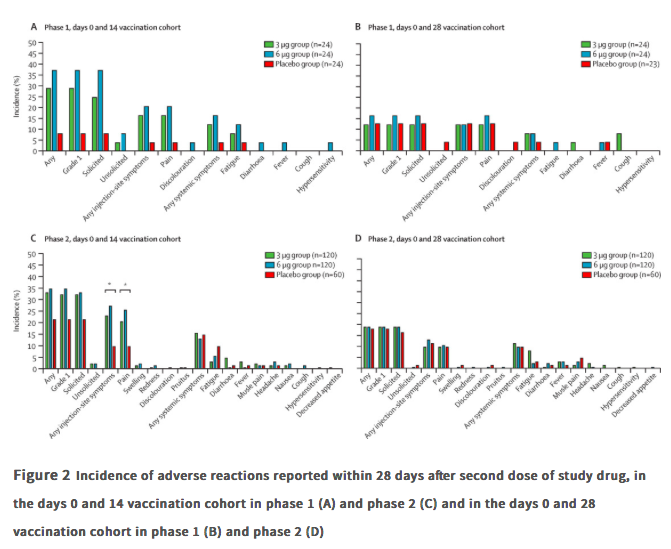
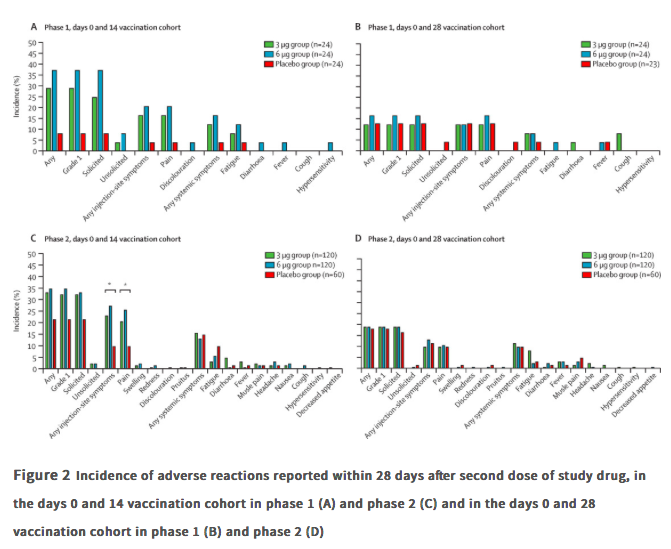
Findings Between April 16 and April 25, 2020, 144 participants were enrolled in the phase 1 trial, and between May 3 and May 5, 2020, 600 participants were enrolled in the phase 2 trial. 743 participants received at least one dose of investigational product (n=143 for phase 1 and n=600 for phase 2; safety population). In the phase 1 trial, the incidence of adverse reactions for the days 0 and 14 cohort was seven (29%) of 24 participants in the 3 ug group, nine (38%) of 24 in the 6 μg group, and two (8%) of 24 in the placebo group, and for the days 0 and 28 cohort was three (13%) of 24 in the 3 μg group, four (17%) of 24 in the 6 μg group, and three (13%) of 23 in the placebo group. The seroconversion of neutralising antibodies on day 14 after the days 0 and 14 vaccination schedule was seen in 11 (46%) of 24 participants in the 3 μg group, 12 (50%) of 24 in the 6 μg group, and none (0%) of 24 in the placebo group; whereas at day 28 after the days 0 and 28 vaccination schedule, seroconversion was seen in 20 (83%) of 24 in the 3 μg group, 19 (79%) of 24 in the 6 μg group, and one (4%) of 24 in the placebo group. In the phase 2 trial, the incidence of adverse reactions for the days 0 and 14 cohort was 40 (33%) of 120 participants in the 3 μg group, 42 (35%) of 120 in the 6 μg group, and 13 (22%) of 60 in the placebo group, and for the days 0 and 28 cohort was 23 (19%) of 120 in the 3 μg group, 23 (19%) of 120 in the 6 μg group, and 11 (18%) of 60 for the placebo group. Seroconversion of neutralising antibodies was seen for 109 (92%) of 118 participants in the 3 μg group, 117 (98%) of 119 in the 6 μg group, and two (3%) of 60 in the placebo group at day 14 after the days 0 and 14 schedule; whereas at day 28 after the days 0 and 28 schedule, seroconversion was seen in 114 (97%) of 117 in the 3 μg group, 118 (100%) of 118 in the 6 μg group, and none (0%) of 59 in the placebo group.
Interpretation Taking safety, immunogenicity, and production capacity into account, the 3 μg dose of CoronaVac is the suggested dose for efficacy assessment in future phase 3 trials.
✦ Safety and efficacy of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous prime-boost COVID-19 vaccine: an interim analysis of a randomised controlled phase 3 trial in Russia.
Référence : https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(21)00234-8/fulltext
Essai de phase 3 sur l’efficacité du vaccin Sputnik V
Résumé article :
Background A heterologous recombinant adenovirus (rAd)-based vaccine, Gam-COVID-Vac (Sputnik V), showed a good safety profile and induced strong humoral and cellular immune responses in participants in phase 1/2 clinical trials. Here, we report preliminary results on the efficacy and safety of Gam-COVID-Vac from the interim analysis of this phase 3 trial.
Methods We did a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial at 25 hospitals and polyclinics in Moscow, Russia. We included participants aged at least 18 years, with negative SARS-CoV-2 PCR and IgG and IgM tests, no infectious diseases in the 14 days before enrolment, and no other vaccinations in the 30 days before enrolment. Participants were randomly assigned (3:1) to receive vaccine or placebo, with stratification by age group. Investigators, participants, and all study staff were masked to group assignment. The vaccine was administered (0·5 mL/dose) intramuscularly in a prime-boost regimen: a 21-day interval between the first dose (rAd26) and the second dose (rAd5), both vectors carrying the gene for the full-length SARS-CoV-2 glycoprotein S. The primary outcome was the proportion of participants with PCR-confirmed COVID-19 from day 21 after receiving the first dose. All analyses excluded participants with protocol violations: the primary outcome was assessed in participants who had received two doses of vaccine or placebo, serious adverse events were assessed in all participants who had received at least one dose at the time of database lock, and rare adverse events were assessed in all participants who had received two doses and for whom all available data were verified in the case report form at the time of database lock. The trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT04530396).
Findings Between Sept 7 and Nov 24, 2020, 21 977 adults were randomly assigned to the vaccine group (n=16 501) or the placebo group (n=5476). 19 866 received two doses of vaccine or placebo and were included in the primary outcome analysis. From 21 days after the first dose of vaccine (the day of dose 2), 16 (0·1%) of 14 964 participants in the vaccine group and 62 (1·3%) of 4902 in the placebo group were confirmed to have COVID-19; vaccine efficacy was 91·6% (95% CI 85·6–95·2). Most reported adverse events were grade 1 (7485 [94·0%] of 7966 total events). 45 (0·3%) of 16 427 participants in the vaccine group and 23 (0·4%) of 5435 participants in the placebo group had serious adverse events; none were considered associated with vaccination, with confirmation from the independent data monitoring committee. Four deaths were reported during the study (three [<0·1%] of 16 427 participants in the vaccine group and one [<0·1%] of 5435 participants in the placebo group), none of which were considered related to the vaccine.
Interpretation This interim analysis of the phase 3 trial of Gam-COVID-Vac showed 91·6% efficacy against COVID-19 and was well tolerated in a large cohort.
✦ Ventilation management and clinical outcomes in invasively ventilated patients with COVID-19 (PRoVENT-COVID): a national, multicentre, observational cohort study.
Référence : https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(20)30459-8/fulltext
Etude rétrospective sur les paramètres de ventilation des patients intubés atteints de COVID-19 aux Pays-Bas.
Résumé article :
Background Little is known about the practice of ventilation management in patients with COVID-19. We aimed to describe the practice of ventilation management and to establish outcomes in invasively ventilated patients with COVID-19 in a single country during the first month of the outbreak.
Methods PRoVENT-COVID is a national, multicentre, retrospective observational study done at 18 intensive care units (ICUs) in the Netherlands. Consecutive patients aged at least 18 years were eligible for participation if they had received invasive ventilation for COVID-19 at a participating ICU during the first month of the national outbreak in the Netherlands. The primary outcome was a combination of ventilator variables and parameters over the first 4 calendar days of ventilation: tidal volume, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), respiratory system compliance, and driving pressure. Secondary outcomes included the use of adjunctive treatments for refractory hypoxaemia and ICU complications. Patient-centred outcomes were ventilator-free days at day 28, duration of ventilation, duration of ICU and hospital stay, and mortality.
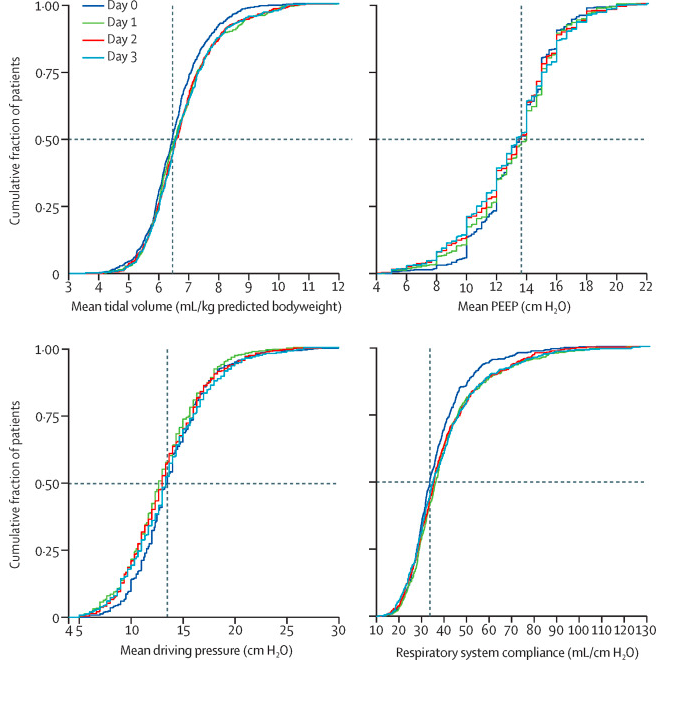
Findings Between March 1 and April 1, 2020, 553 patients were included in the study. Median tidal volume was 6·3 mL/kg predicted bodyweight (IQR 5·7–7·1), PEEP was 14·0 cm H2O (IQR 11·0–15·0), and driving pressure was 14·0 cm H2O (11·2–16·0). Median respiratory system compliance was 31·9 mL/cm H2O (26·0–39·9). Of the adjunctive treatments for refractory hypoxaemia, prone positioning was most often used in the first 4 days of ventilation (283 [53%] of 530 patients). The median number of ventilator-free days at day 28 was 0 (IQR 0–15); 186 (35%) of 530 patients had died by day 28. Predictors of 28-day mortality were gender, age, tidal volume, respiratory system compliance, arterial pH, and heart rate on the first day of invasive ventilation.
Interpretation In patients with COVID-19 who were invasively ventilated during the first month of the outbreak in the Netherlands, lung-protective ventilation with low tidal volume and low driving pressure was broadly applied and prone positioning was often used. The applied PEEP varied widely, despite an invariably low respiratory system compliance. The findings of this national study provide a basis for new hypotheses and sample size calculations for future trials of invasive ventilation for COVID-19. These data could also help in the interpretation of findings from other studies of ventilation practice and outcomes in invasively ventilated patients with COVID-19.
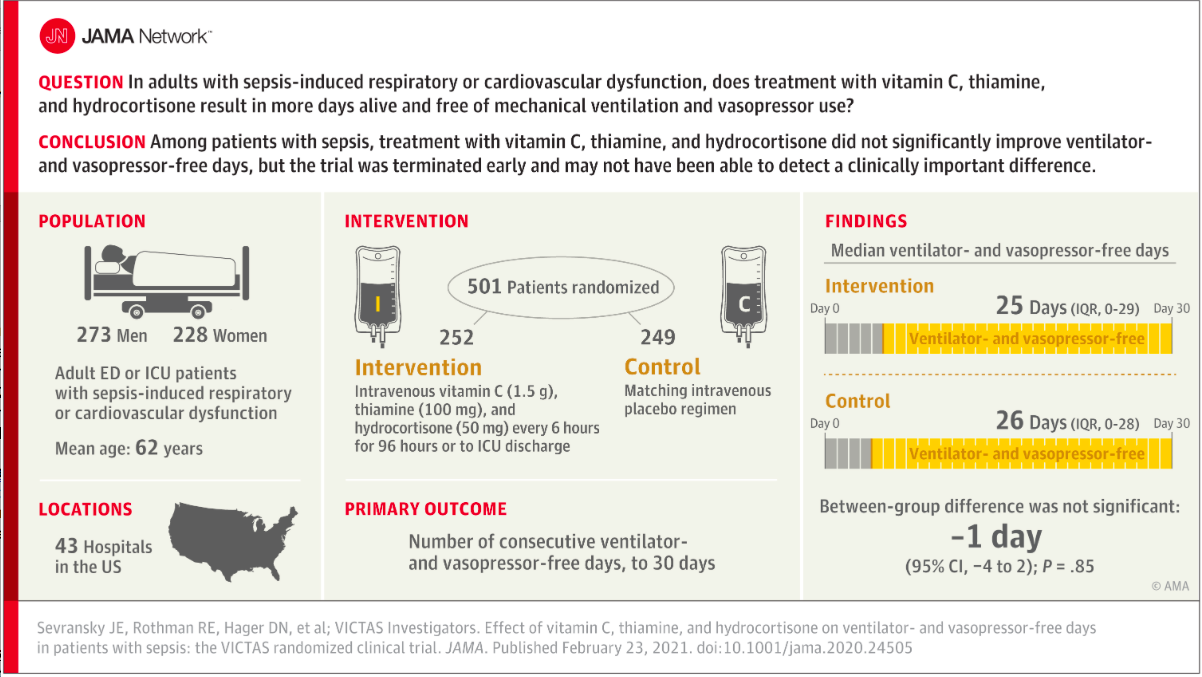
✦ Effect of Vitamin C, Thiamine, and Hydrocortisone on Ventilator- and Vasopressor-Free Days in Patients With SepsisThe VICTAS Randomized Clinical Trial
Référence : 10.1001/jama.2020.24505
Résumé article :
Importance Sepsis is a common syndrome with substantial morbidity and mortality. A combination of vitamin C, thiamine, and corticosteroids has been proposed as a potential treatment for patients with sepsis.
Objective To determine whether a combination of vitamin C, thiamine, and hydrocortisone every 6 hours increases ventilator- and vasopressor-free days compared with placebo in patients with sepsis.
Design, Setting, and Participants Multicenter, randomized, double-blind, adaptive-sample-size, placebo-controlled trial conducted in adult patients with sepsis-induced respiratory and/or cardiovascular dysfunction. Participants were enrolled in the emergency departments or intensive care units at 43 hospitals in the United States between August 2018 and July 2019. After enrollment of 501 participants, funding was withheld, leading to an administrative termination of the trial. All study-related follow-up was completed by January 2020.
Interventions Participants were randomized to receive intravenous vitamin C (1.5 g), thiamine (100 mg), and hydrocortisone (50 mg) every 6 hours (n = 252) or matching placebo (n = 249) for 96 hours or until discharge from the intensive care unit or death. Participants could be treated with open-label corticosteroids by the clinical team, with study hydrocortisone or matching placebo withheld if the total daily dose was greater or equal to the equivalent of 200 mg of hydrocortisone.
Main Outcomes and Measures The primary outcome was the number of consecutive ventilator- and vasopressor-free days in the first 30 days following the day of randomization. The key secondary outcome was 30-day mortality.
Results Among 501 participants randomized (median age, 62 [interquartile range {IQR}, 50-70] years; 46% female; 30% Black; median Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II score, 27 [IQR, 20.8-33.0]; median Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score, 9 [IQR, 7-12]), all completed the trial. Open-label corticosteroids were prescribed to 33% and 32% of the intervention and control groups, respectively. Ventilator- and vasopressor-free days were a median of 25 days (IQR, 0-29 days) in the intervention group and 26 days (IQR, 0-28 days) in the placebo group, with a median difference of −1 day (95% CI, −4 to 2 days; P = .85). Thirty-day mortality was 22% in the intervention group and 24% in the placebo group.
Conclusions and Relevance Among critically ill patients with sepsis, treatment with vitamin C, thiamine, and hydrocortisone, compared with placebo, did not significantly increase ventilator- and vasopressor-free days within 30 days. However, the trial was terminated early for administrative reasons and may have been underpowered to detect a clinically important difference.
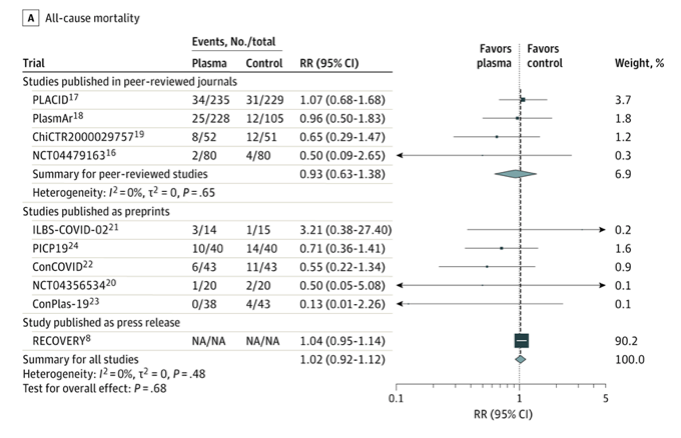
✦ Association of Convalescent Plasma Treatment With Clinical Outcomes in Patients With COVID-19A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Référence : 10.1001/jama.2021.2747
Résumé article :
Importance Convalescent plasma is a proposed treatment for COVID-19.
Objective To assess clinical outcomes with convalescent plasma treatment vs placebo or standard of care in peer-reviewed and preprint publications or press releases of randomized clinical trials (RCTs).
Data Sources PubMed, the Cochrane COVID-19 trial registry, and the Living Overview of Evidence platform were searched until January 29, 2021.
Study Selection The RCTs selected compared any type of convalescent plasma vs placebo or standard of care for patients with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 in any treatment setting.
Data Extraction and Synthesis Two reviewers independently extracted data on relevant clinical outcomes, trial characteristics, and patient characteristics and used the Cochrane Risk of Bias Assessment Tool. The primary analysis included peer-reviewed publications of RCTs only, whereas the secondary analysis included all publicly available RCT data (peer-reviewed publications, preprints, and press releases). Inverse variance–weighted meta-analyses were conducted to summarize the treatment effects. The certainty of the evidence was assessed using the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation.
Main Outcomes and Measures All-cause mortality, length of hospital stay, clinical improvement, clinical deterioration, mechanical ventilation use, and serious adverse events.
Results A total of 1060 patients from 4 peer-reviewed RCTs and 10 722 patients from 6 other publicly available RCTs were included. The summary risk ratio (RR) for all-cause mortality with convalescent plasma in the 4 peer-reviewed RCTs was 0.93 (95% CI, 0.63 to 1.38), the absolute risk difference was −1.21% (95% CI, −5.29% to 2.88%), and there was low certainty of the evidence due to imprecision. Across all 10 RCTs, the summary RR was 1.02 (95% CI, 0.92 to 1.12) and there was moderate certainty of the evidence due to inclusion of unpublished data. Among the peer-reviewed RCTs, the summary hazard ratio was 1.17 (95% CI, 0.07 to 20.34) for length of hospital stay, the summary RR was 0.76 (95% CI, 0.20 to 2.87) for mechanical ventilation use (the absolute risk difference for mechanical ventilation use was −2.56% [95% CI, −13.16% to 8.05%]), and there was low certainty of the evidence due to imprecision for both outcomes. Limited data on clinical improvement, clinical deterioration, and serious adverse events showed no significant differences.
Conclusions and Relevance Treatment with convalescent plasma compared with placebo or standard of care was not significantly associated with a decrease in all-cause mortality or with any benefit for other clinical outcomes. The certainty of the evidence was low to moderate for all-cause mortality and low for other outcomes.
✦ Association of Early vs Late Tracheostomy Placement With Pneumonia and Ventilator Days in Critically Ill Patients : A Meta-analysis
Référence : 10.1001/jamaoto.2021.0025
Résumé article :
Importance The timing of tracheostomy placement in adult patients undergoing critical care remains unestablished. Previous meta-analyses have reported mixed findings regarding early vs late tracheostomy placement for ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), ventilator days, mortality, and length of intensive care unit (ICU) hospitalization.
Objective To compare the association of early (≤7 days) vs late tracheotomy with VAP and ventilator days in critically ill adults.
Data Sources A search of MEDLINE, CINAHL, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, references of relevant articles, previous meta-analyses, and gray literature from inception to March 31, 2020, was performed.
Study Selection Randomized clinical trials comparing early and late tracheotomy with any of our primary outcomes, VAP or ventilator days, were included.
Data Extraction and Synthesis Two independent reviewers conducted all stages of the review. The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses guideline was followed. Pooled odds ratios (ORs) or the mean difference (MD) with 95% CIs were calculated using a random-effects model.
Main Outcomes and Measures Primary outcomes included VAP and duration of mechanical ventilation. Intensive care unit days and mortality (within the first 30 days of hospitalization) constituted secondary outcomes.
Results Seventeen unique trials with a cumulative 3145 patients (mean [SD] age range, 32.9 [12.7] to 67.9 [17.6] years) were included in this review. Individuals undergoing early tracheotomy had a decrease in the occurrence of VAP (OR, 0.59 [95% CI, 0.35-0.99]; 1894 patients) and experienced more ventilator-free days (MD, 1.74 [95% CI, 0.48-3.00] days; 1243 patients). Early tracheotomy also resulted in fewer ICU days (MD, −6.25 [95% CI, −11.22 to −1.28] days; 2042 patients). Mortality was reported for 2445 patients and was comparable between groups (OR, 0.66 [95% CI, 0.38-1.15]).
Conclusions and Relevance Compared with late tracheotomy, early intervention was associated with lower VAP rates and shorter durations of mechanical ventilation and ICU stay, but not with reduced short-term, all-cause mortality. These findings have substantial clinical implications and may result in practice changes regarding the timing of tracheotomy in severely ill adults requiring mechanical ventilation.
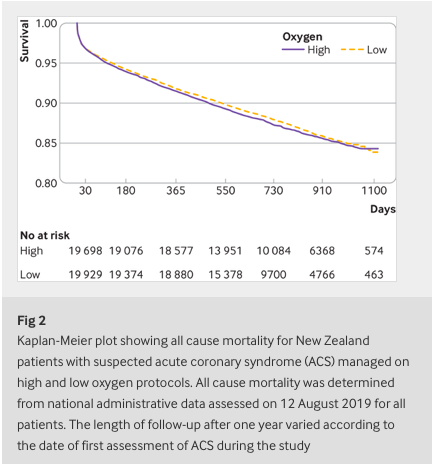
✦ High flow oxygen and risk of mortality in patients with a suspected acute coronary syndrome: pragmatic, cluster randomised, crossover trial
Référence : https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n355
Résumé article :
Objective To determine the association between high flow supplementary oxygen and 30 day mortality in patients presenting with a suspected acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Design Pragmatic, cluster randomised, crossover trial.
Setting Four geographical regions in New Zealand.
Participants 40 872 patients with suspected or confirmed ACS included in the All New Zealand Acute Coronary Syndrome Quality Improvement registry or ambulance ACS pathway during the study periods. 20 304 patients were managed using the high oxygen protocol and 20 568 were managed using the low oxygen protocol. Final diagnosis of ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non-STEMI were determined from the registry and ICD-10 discharge codes.
Interventions The four geographical regions were randomly allocated to each of two oxygen protocols in six month blocks over two years. The high oxygen protocol recommended oxygen at 6-8 L/min by face mask for ischaemic symptoms or electrocardiographic changes, irrespective of the transcapillary oxygen saturation (SpO2). The low oxygen protocol recommended oxygen only if SpO2 was less than 90%, with a target SpO2 of less than 95%.
Main outcome measure 30 day all cause mortality determined from linkage to administrative data.
Results Personal and clinical characteristics of patients managed under both oxygen protocols were well matched. For patients with suspected ACS, 30 day mortality for the high and low oxygen groups was 613 (3.0%) and 642 (3.1%), respectively (odds ratio 0.97, 95% confidence interval 0.86 to 1.08). For 4159 (10%) patients with STEMI, 30 day mortality for the high and low oxygen groups was 8.8% (n=178) and 10.6% (n=225), respectively (0.81, 0.66 to 1.00) and for 10 218 (25%) patients with non-STEMI was 3.6% (n=187) and 3.5% (n=176), respectively (1.05, 0.85 to 1.29).
Conclusion In a large patient cohort presenting with suspected ACS, high flow oxygen was not associated with an increase or decrease in 30 day mortality.
LES 100% ANESTHÉSIE :
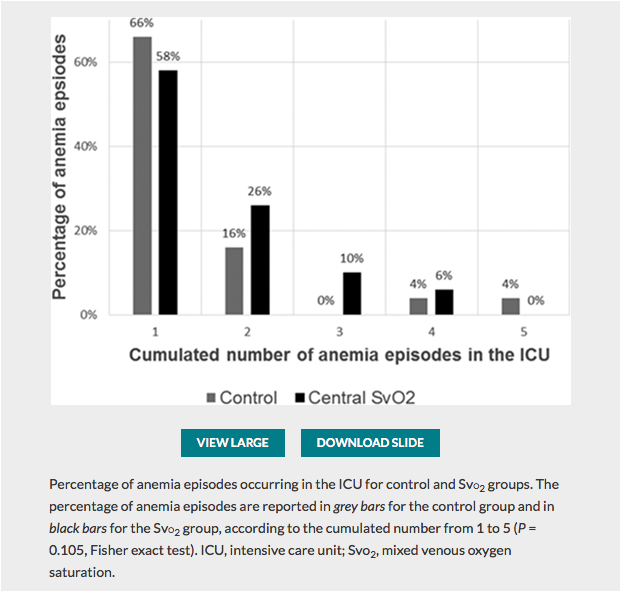
✦ Restrictive Transfusion Strategy after Cardiac Surgery: Role of Central Venous Oxygen Saturation Trigger: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Référence : 10.1097/ALN.0000000000003682
La transfusion est une décision thérapeutique qui peut avoir des conséquences pour le patient. La reflexion sur la prise de décision peut etre affinée par l’utilisation de la SCVO2. Un seuil est donc moins pertinent qu’un rationnel physiologique ciblant l’adéquation du TaO2 à la consomation d’O2 par l’organisme. A lire également l’éditorial Known and Unknown Unknowns in Making Erythrocyte Transfusion Decisions qui lui est consacré.
Résumé article :
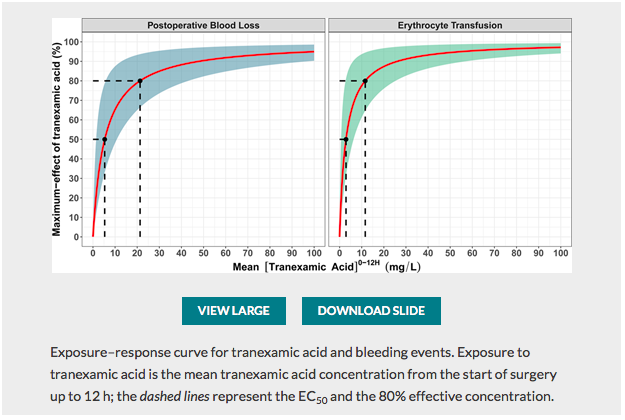
✦ Exposure–Response Relationship of Tranexamic Acid in Cardiac Surgery: A Model-based Meta-analysis
Référence : 10.1097/ALN.0000000000003633
Travail sur l’optimisation de la posologie d’acide tranexamique , majorer l’efficacité et donc la réduction des pertes sanguines tout en minimisant les risques d’effets secondaires du traitement (épilepsie) associé à un édito Optimal Tranexamic Acid Dosing Regimen in Cardiac Surgery: What Are the Missing Pieces? qui met en perspective ces résultats.
Résumé article :
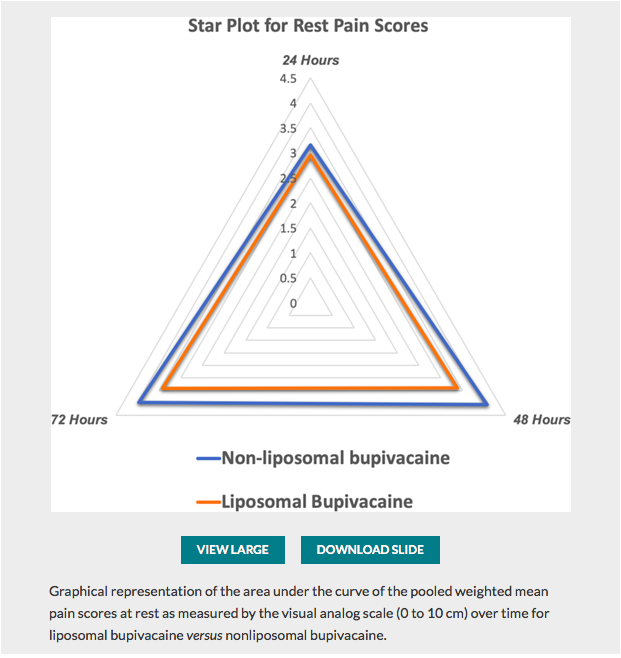
✦ Perineural Liposomal Bupivacaine Is Not Superior to Nonliposomal Bupivacaine for Peripheral Nerve Block Analgesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Référence : 10.1097/ALN.0000000000003651
Quelques lignes de présentations : La bupivacaine liposomal à fait l’objet de plusieurs études pour tenter de prouver sa supériorité en terme d’efficacité et de durée d’action. Cette méta-analyse fait le point sur ces données.
Résumé article :
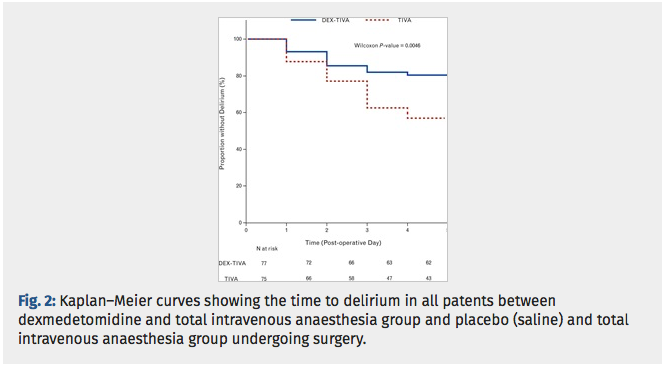
✦ Dexmedetomidine for prevention of postoperative delirium in older adults undergoing oesophagectomy with total intravenous anaesthesia. A double-blind, randomised clinical trial.
Référence / doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000001382.
Dexmet est connue pour être un sédatif. Les études récentes suggèrent que l’administration de dexemetomdine peur prévenir le délirium post opératoire. Cette étude évalue les effets de la dexemet sur les patients âgés subissant une oesophagectomie avec abord thoracique sous anésthesie intraveineuse totale versus ceux bénéficiant dune anesthésie IV totale + dexemet.
Etude controlée randomisée, critère de jugement principal est l’incidence du delirium post opératoire.
Le groupe DEXMET + anesthésie iv totale comprenait significativement moins de patients ayant un delirium post op que le groupe anesthésie iv seule.
Posologie de la dexmet : bolus 0,4 ml/kg pendant 15 minutes puis 0,1 ml/kg.
Dépistage du delirium post opératoire :échelle RSA Riker Sedation Agitation
Résumé article :
Background: Dexmedetomidine is known to be a sedative. Recent studies suggest that administration of dexmedetomidine can prevent postoperative delirium (POD) which has been confirmed as a common complication after major surgery. However, its effects in patients undergoing oesophagectomy are scarce.
Objective: To investigate the efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine in reducing POD in elderly patients after transthoracic oesophagectomy with total intravenous anaesthesia (TIVA).
Design: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
Setting: Single-centre, tertiary care hospital, November 2016 to September 2018.
Patients: Eligible patients (n = 177) undergoing transthoracic oesophagectomy were randomly assigned to receive total intravenous anaesthesia (TIVA, n = 87) or dexmedetomidine with TIVA (DEX-TIVA, n = 90).
Interventions: Patients receiving DEX-TIVA received a loading dose of dexmedetomidine (0.4 μg kg-1), over 15 min, followed by a continuous infusion at a rate of 0.1 μg kg-1 h-1 until 1 h before the end of surgery. Patients receiving TIVA received physiological saline with a similar infusion rate protocol.
Outcome measures: The primary outcome was the incidence of POD. The secondary endpoints were the incidence of emergence agitation, serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) levels and haemodynamic profile.
Results: All randomised patients were included with planned intention-to-treat analyses for POD. Delirium occurred in 15 (16.7%) of 90 cases given dexmedetomidine, and in 32 (36.8%) of 87 cases given saline (P = 0.0036). The DEX-TIVA group showed less frequent emergence agitation than the TIVA group (22.1 vs. 48.0%, P = 0.0058). The incremental change in surgery-induced IL-6 levels was greater in the TIVA group than DEX-TIVA group (P < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Adding peri-operative dexmedetomidine to a total intravenous anaesthetic safely reduces POD and emergence agitation in elderly patients undergoing open transthoracic oesophagectomy. These benefits were associated with a postoperative reduction in circulating levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 and stabilisation of the haemodynamic profile.
✦ Prevention of Cardiac Surgery–Associated Acute Kidney Injury by Implementing the KDIGO Guidelines in High-Risk Patients Identified by Biomarkers: The PrevAKI-Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial
Référence / doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000005458
Résumé article :
Background Prospective, single-center trials have shown that the implementation of the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) recommendations in high-risk patients significantly reduced the development of acute kidney injury (AKI) after surgery. We sought to evaluate the feasibility of implementing a bundle of supportive measures based on the KDIGO guideline in high-risk patients undergoing cardiac surgery in a multicenter setting in preparation for a large definitive trial.
Methods In this multicenter, multinational, randomized controlled trial, we examined the adherence to the KDIGO bundle consisting of optimization of volume status and hemodynamics, functional hemodynamic monitoring, avoidance of nephrotoxic drugs, and prevention of hyperglycemia in high-risk patients identified by the urinary biomarkers tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 [TIMP-2] and insulin growth factor–binding protein 7 [IGFBP7] after cardiac surgery. The primary end point was the adherence to the bundle protocol and was evaluated by the percentage of compliant patients with a 95% confidence interval (CI) according to Clopper-Pearson. Secondary end points included the development and severity of AKI.
Results In total, 278 patients were included in the final analysis. In the intervention group, 65.4% of patients received the complete bundle as compared to 4.2% in the control group (absolute risk reduction [ARR] 61.2 [95% CI, 52.6-69.9]; P < .001). AKI rates were statistically not different in both groups (46.3% intervention versus 41.5% control group; ARR −4.8% [95% CI, −16.4 to 6.9]; P = .423). However, the occurrence of moderate and severe AKI was significantly lower in the intervention group as compared to the control group (14.0% vs 23.9%; ARR 10.0% [95% CI, 0.9-19.1]; P = .034). There were no significant effects on other specified secondary outcomes.
Conclusions Implementation of a KDIGO-derived treatment bundle is feasible in a multinational setting. Furthermore, moderate to severe AKI was significantly reduced in the intervention group.
LES 100% RÉANIMATION :
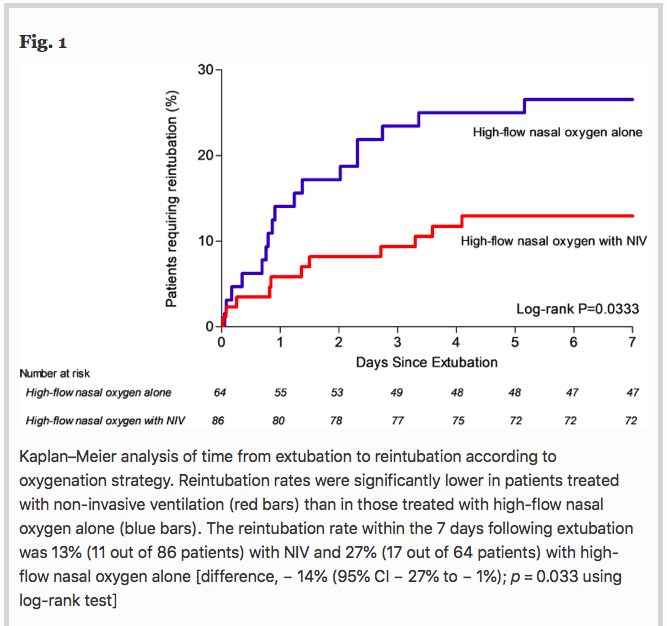
✦ Non-invasive ventilation alternating with high-flow nasal oxygen versus high-flow nasal oxygen alone after extubation in COPD patients: a post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial
Référence : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-021-00823-7
La gestion post extubation des patients BPCO est assez complexe, avec un risque d’oedème pulmonaire de sevrage. Est ce la VNI en plus de l’optiflow diminuerait le risque de réintubation ?
Résumé article :
Background Several randomized clinical trials have shown that non-invasive ventilation (NIV) applied immediately after extubation may prevent reintubation in patients at high-risk of extubation failure. However, most of studies included patients with chronic respiratory disorders as well as patients without underlying respiratory disease. To date, no study has shown decreased risk of reintubation with prophylactic NIV after extubation among patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). We hypothesized that prophylactic NIV after extubation may decrease the risk of reintubation in COPD patients as compared with high-flow nasal oxygen. We performed a post hoc subgroup analysis of COPD patients included in a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial comparing prophylactic use of NIV alternating with high-flow nasal oxygen versus high-flow nasal oxygen alone immediately after extubation.
Results Among the 651 patients included in the original study, 150 (23%) had underlying COPD including 86 patients treated with NIV alternating with high-flow nasal oxygen and 64 patients treated with high-flow nasal oxygen alone. The reintubation rate was 13% (11 out of 86 patients) with NIV and 27% (17 out of 64 patients) with high-flow nasal oxygen alone [difference, − 14% (95% CI − 27% to − 1%); p = 0.03]. Whereas reintubation rates were significantly lower with NIV than with high-flow nasal oxygen alone at 72 h and until ICU discharge, mortality in ICU did not differ between groups: 6% (5/86) with NIV vs. 9% (6/64) with high-flow nasal oxygen alone [difference − 4% (95% CI − 14% to 5%); p = 0.40].
Conclusions In COPD patients, prophylactic NIV alternating with high-flow nasal oxygen significantly decreased the risk of reintubation compared with high-flow nasal oxygen alone.
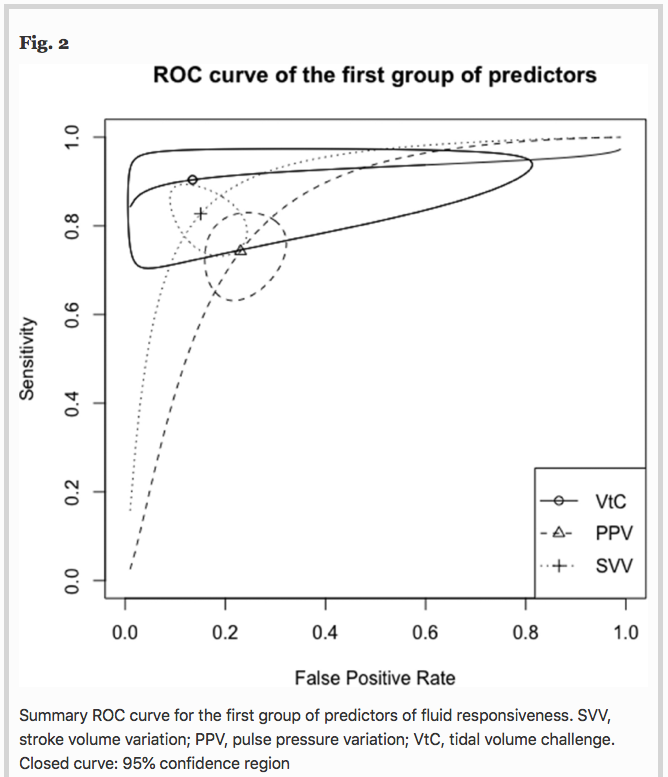
✦ Predictors of fluid responsiveness in critically ill patients mechanically ventilated at low tidal volumes: systematic review and meta-analysis
Référence : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-021-00817-5
Les critères de précharge dépendance sont souvent validés pour les patients ventilés mécaniquement à > 8 mL/kg de Vt, mais dans le contexte actuel où y’a plus de SDRA que jamais, quels sont les indicateurs de précharge dépendance utilisable quand on est à 6mL/kg de Vt ?
Résumé article :
Introduction Dynamic predictors of fluid responsiveness have shown good performance in mechanically ventilated patients at tidal volumes (Vt) > 8 mL kg−1. Nevertheless, most critically ill conditions demand lower Vt. We sought to evaluate the operative performance of several predictors of fluid responsiveness at Vt ≤ 8 mL kg−1 by using meta-regression and subgroup analyses.
Methods A sensitive search was conducted in the Embase and MEDLINE databases. We searched for studies prospectively assessing the operative performance of pulse pressure variation (PPV), stroke volume variation (SVV), end-expiratory occlusion test (EEOT), passive leg raising (PLR), inferior vena cava respiratory variability (Δ-IVC), mini-fluid challenge (m-FC), and tidal volume challenge (VtC), to predict fluid responsiveness in adult patients mechanically ventilated at Vt ≤ 8 ml kg−1, without respiratory effort and arrhythmias, published between 1999 and 2020. Operative performance was assessed using hierarchical and bivariate analyses, while subgroup analysis was used to evaluate variations in their operative performance and sources of heterogeneity. A sensitivity analysis based on the methodological quality of the studies included (QUADAS-2) was also performed.
Results A total of 33 studies involving 1,352 patients were included for analysis. Areas under the curve (AUC) values for predictors of fluid responsiveness were: for PPV = 0.82, Δ-IVC = 0.86, SVV = 0.90, m-FC = 0.84, PLR = 0.84, EEOT = 0.92, and VtC = 0.92. According to subgroup analyses, variations in methods to measure cardiac output and in turn, to classify patients as responders or non-responders significantly influence the performance of PPV and SVV (p < 0.05). Operative performance of PPV was also significantly affected by the compliance of the respiratory system (p = 0.05), while type of patient (p < 0.01) and thresholds used to determine responsiveness significantly affected the predictability of SVV (p = 0.05). Similarly, volume of fluids infused to determine variation in cardiac output, significantly affected the performance of SVV (p = 0.01) and PLR (p < 0.01). Sensitivity analysis showed no variations in operative performance of PPV (p = 0.39), SVV (p = 0.23) and EEOT (p = 0.15).
Conclusion Most predictors of fluid responsiveness reliably predict the response of cardiac output to volume expansion in adult patients mechanically ventilated at tidal volumes ≤ 8 ml kg−1. Nevertheless, technical and clinical variables might clearly influence on their operative performance
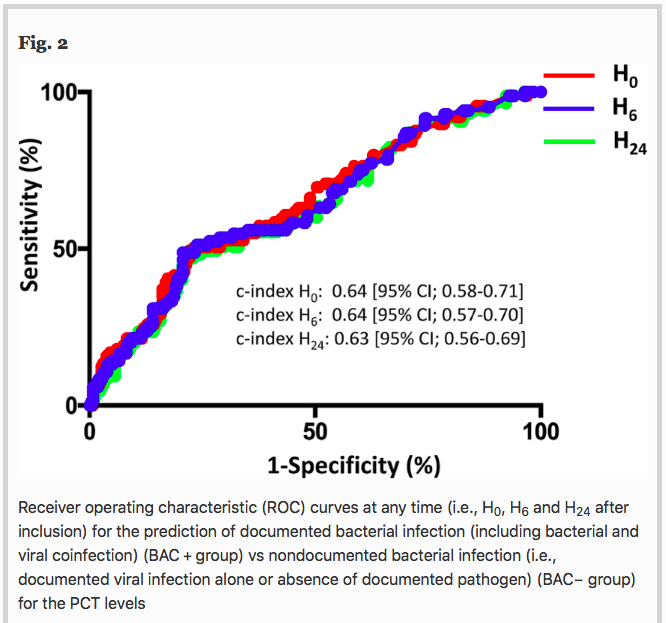
✦ Ability of procalcitonin to distinguish between bacterial and nonbacterial infection in severe acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary syndrome in the ICU
Référence : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-021-00816-6
Petite gueguerre sur la PCT, spécifique ou non d’une infection bactérienne ? Etude ici chez les patients avec exacerbation sévère de BPCO
Résumé article :
Background To assess the ability of procalcitonin (PCT) to distinguish between bacterial and nonbacterial causes of patients with severe acute exacerbation of COPD (AECOPD) admitted to the ICU, we conducted a retrospective analysis of two prospective studies including 375 patients with severe AECOPD with suspected lower respiratory tract infections. PCT levels were sequentially assessed at the time of inclusion, 6 h after and at day 1, using a sensitive immunoassay. The patients were classified according to the presence of a documented bacterial infection (including bacterial and viral coinfection) (BAC + group), or the absence of a documented bacterial infection (i.e., a documented viral infection alone or absence of a documented pathogen) (BAC- group). The accuracy of PCT levels in predicting bacterial infection (BAC + group) vs no bacterial infection (BAC- group) at different time points was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis.
Results Regarding the entire cohort (n = 375), at any time, the PCT levels significantly differed between groups (Kruskal–Wallis test, p < 0.001). A pairwise comparison showed that PCT levels were significantly higher in patients with bacterial infection (n = 94) than in patients without documented pathogens (n = 218) (p < 0.001). No significant difference was observed between patients with bacterial and viral infection (n = 63). For example, the median PCT-H0 levels were 0.64 ng/ml [0.22–0.87] in the bacterial group vs 0.24 ng/ml [0.15–0.37] in the viral group and 0.16 ng/mL [0.11–0.22] in the group without documented pathogens. With a c-index of 0.64 (95% CI; 0.58–0.71) at H0, 0.64 [95% CI 0.57–0.70] at H6 and 0.63 (95% CI; 0.56–0.69) at H24, PCT had a low accuracy for predicting bacterial infection (BAC + group).
Conclusion Despite higher PCT levels in severe AECOPD caused by bacterial infection, PCT had a poor accuracy to distinguish between bacterial and nonbacterial infection. Procalcitonin might not be sufficient as a standalone marker for initiating antibiotic treatment in this setting.
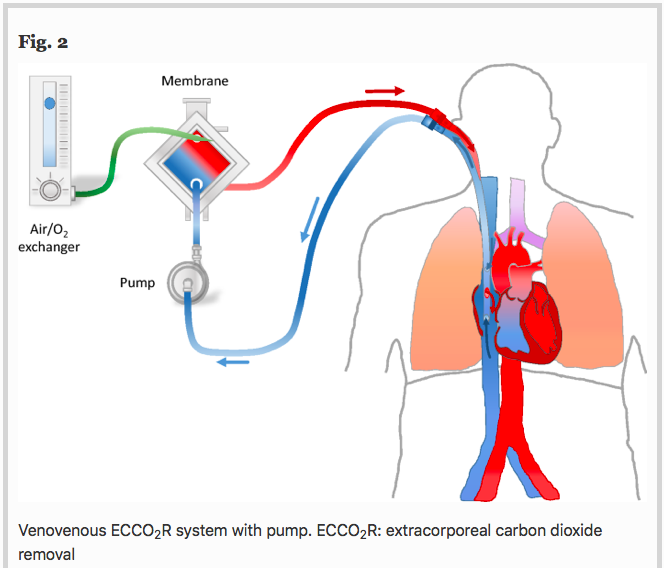
✦ The use of extracorporeal CO2 removal in acute respiratory failure
Référence : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13613-021-00824-6
Une technologie un peu moins connue qu’est l’ECCO2R, une ECLS à bas débit qui ne sert qu’à décarboxyler (et non à oxygéner … “officiellement”)
Résumé article :
Background Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation and protective mechanical ventilation of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) patients induce hypercapnic respiratory acidosis.
Main text Extracorporeal carbon dioxide removal (ECCO2R) aims to eliminate blood CO2 to fight against the adverse effects of hypercapnia and related acidosis. Hypercapnia has deleterious extrapulmonary consequences, particularly for the brain. In addition, in the lung, hypercapnia leads to: lower pH, pulmonary vasoconstriction, increases in right ventricular afterload, acute cor pulmonale. Moreover, hypercapnic acidosis may further damage the lungs by increasing both nitric oxide production and inflammation and altering alveolar epithelial cells. During an exacerbation of COPD, relieving the native lungs of at least a portion of the CO2 could potentially reduce the patient’s respiratory work, Instead of mechanically increasing alveolar ventilation with MV in an already hyperinflated lung to increase CO2 removal, the use of ECCO2R may allow a decrease in respiratory volume and respiratory rate, resulting in improvement of lung mechanic. Thus, the use of ECCO2R may prevent noninvasive ventilation failure and allow intubated patients to be weaned off mechanical ventilation. In ARDS patients, ECCO2R may be used to promote an ultraprotective ventilation in allowing to lower tidal volume, plateau (Pplat) and driving pressures, parameters that have identified as a major risk factors for mortality. However, although ECCO2R appears to be effective in improving gas exchange and possibly in reducing the rate of endotracheal intubation and allowing more protective ventilation, its use may have pulmonary and hemodynamic consequences and may be associated with complications.
Conclusion In selected patients, ECCO2R may be a promising adjunctive therapeutic strategy for the management of patients with severe COPD exacerbation and for the establishment of protective or ultraprotective ventilation in patients with ARDS without prognosis-threatening hypoxemia.
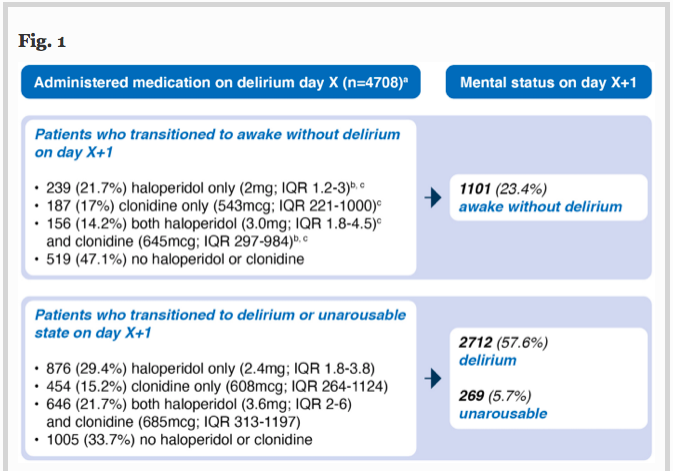
✦ Haloperidol, clonidine and resolution of delirium in critically ill patients: a prospective cohort study
Référence :DOI : 0.1007/s00134-021-06355-9
Résumé article :
Haloperidol et clonidine sont utilisés pour traiter l’agitation en unité de soins intensifs, mais les agents permettant de réduire sa durée restent incertains.
L’objectif de cette étude est de déterminer qui de l’haloperidol, de la clonidine ou des deux combinés reduit le délirium de façon la plus efficace.
Etude de cohorte, critère de jugement principal est la probabilité de résolution du délirium.
Probabilité de résolution du delirium moindre chez les patients recevant de l’haloperidol, de la clonidine ou les deux versus les patients non traités. Les patients recevant ces traitements avaient des durées de delirium plus longues, plus de jours sous ventilations invasives et passaient plus de temps en soins intensifs. Pas de différence notée en terme de mortalité.
L’utilisation d’haloperidol et de clonidine chez les patients ayant un delirium en unités de soins intensifs est associée à une probabilité de résolution plus faible.
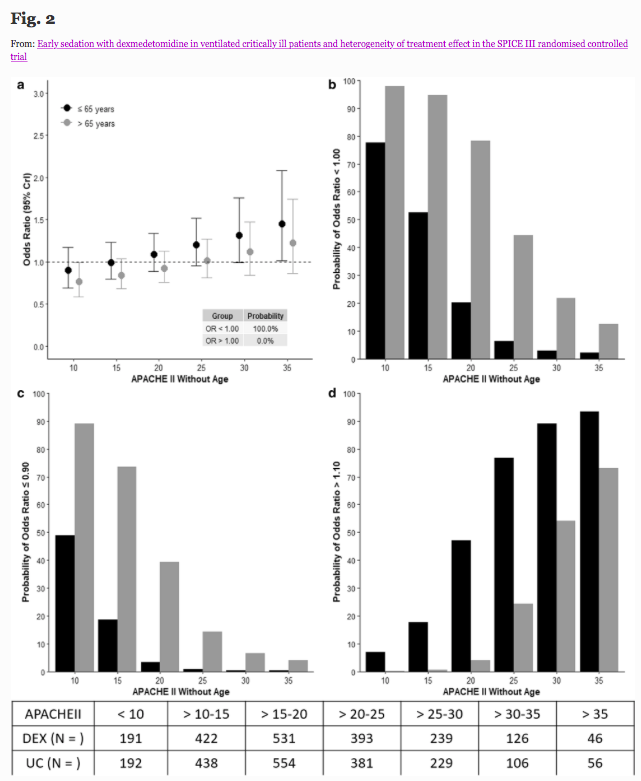
✦ Early sedation with dexmedetomidine in ventilated critically ill patients and heterogeneity of treatment effect in the SPICE III randomised controlled trial
Référence : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00134-021-06356-8
Résumé article :
Purpose To quantify potential heterogeneity of treatment effect (HTE), of early sedation with dexmedetomidine (DEX) compared with usual care, and identify patients who have a high probability of lower or higher 90-day mortality according to age, and other identified clusters.
Methods Bayesian analysis of 3904 critically ill adult patients expected to receive invasive ventilation > 24 h and enrolled in a multinational randomized controlled trial comparing early DEX with usual care sedation.
Results HTE was assessed according to age and clusters (based on 12 baseline characteristics) using a Bayesian hierarchical models. DEX was associated with lower 90-day mortality compared to usual care in patients > 65 years (odds ratio [OR], 0.83 [95% credible interval [CrI] 0.68–1.00], with 97.7% probability of reduced mortality across broad categories of illness severity. Conversely, the probability of increased mortality in patients ≤ 65 years was 98.5% (OR 1.26 [95% CrI 1.02–1.56]. Two clusters were identified: cluster 1 (976 patients) mostly operative, and cluster 2 (2346 patients), predominantly non-operative. There was a greater probability of benefit with DEX in cluster 1 (OR 0.86 [95% CrI 0.65–1.14]) across broad categories of age, with 86.4% probability that DEX is more beneficial in cluster 1 than cluster 2.
Conclusion In critically ill mechanically ventilated patients, early sedation with dexmedetomidine exhibited a high probability of reduced 90-day mortality in older patients regardless of operative or non-operative cluster status. Conversely, a high probability of increased 90-day mortality was observed in younger patients of non-operative status. Further studies are needed to confirm these findings.
✦ Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation–associated Lung Edema (CRALE). A Translational Study
Référence : https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201912-2454OC
Evaluation des lésions pulmonaires post réanimation cardio-pulmonaire.
Résumé article :
Rationale Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is the cornerstone of cardiac arrest (CA) treatment. However, lung injuries associated with it have been reported.
Objectives To assess 1) the presence and characteristics of lung abnormalities induced by cardiopulmonary resuscitation and 2) the role of mechanical and manual chest compression (CC) in its development.
Methods This translational study included 1) a porcine model of CA and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (n = 12) and 2) a multicenter cohort of patients with out-of-hospital CA undergoing mechanical or manual CC (n = 52). Lung computed tomography performed after resuscitation was assessed qualitatively and quantitatively along with respiratory mechanics and gas exchanges.
Measurements and Main Results The lung weight in the mechanical CC group was higher compared with the manual CC group in the experimental (431 ± 127 vs. 273 ± 66, P = 0.022) and clinical study (1,208 ± 630 vs. 837 ± 306, P = 0.006). The mechanical CC group showed significantly lower oxygenation (P = 0.043) and respiratory system compliance (P < 0.001) compared with the manual CC group in the experimental study. The variation of right atrial pressure was significantly higher in the mechanical compared with the manual CC group (54 ± 11 vs. 31 ± 6 mm Hg, P = 0.001) and significantly correlated with lung weight (r = 0.686, P = 0.026) and respiratory system compliance (r = −0.634, P = 0.027). Incidence of abnormal lung density was higher in patients treated with mechanical compared with manual CC (37% vs. 8%, P = 0.018).
Conclusions This study demonstrated the presence of cardiopulmonary resuscitation–associated lung edema in animals and in patients with out-of-hospital CA, which is more pronounced after mechanical as opposed to manual CC and correlates with higher swings of right atrial pressure during CC.
✦ Trends in clinical profiles, organ support use and outcomes of patients with cancer requiring unplanned ICU admission: a multicenter cohort study
Référence : 10.1007/s00134-020-06252-7
Les patients atteints de cancer peuvent être admis en réanimation de manière imprévue. Quelle est la tendance vis à vis du pronostic chez ces patients?
Résumé article :
Introduction To describe trends in outcomes of cancer patients with unplanned admissions to intensive-care units (ICU) according to cancer type, organ support use, and performance status (PS) over an 8-year period.
Method We retrospectively analyzed prospectively collected data from all cancer patients admitted to 92 medical–surgical ICUs from July/2011 to June/2019. We assessed trends in mortality through a Bayesian hierarchical model adjusted for relevant clinical confounders and whether there was a reduction in ICU length-of-stay (LOS) over time using a competing risk model.
Results 32,096 patients (8.7% of all ICU admissions; solid tumors, 90%; hematological malignancies, 10%) were studied. Bed/days use by cancer patients increased up to more than 30% during the period. Overall adjusted mortality decreased by 9.2% [95% credible interval (CI), 13.1–5.6%]. The largest reductions in mortality occurred in patients without need for organ support (9.6%) and in those with need for mechanical ventilation (MV) only (11%). Smallest reductions occurred in patients requiring MV, vasopressors, and dialysis (3.9%) simultaneously. Survival gains over time decreased as PS worsened. Lung cancer patients had the lowest decrease in mortality. Each year was associated with a lower sub-hazard for ICU death [SHR 0.93 (0.91–0.94)] and a higher chance of being discharged alive from the ICU earlier [SHR 1.01 (1–1.01)].
Conclusion Outcomes in critically ill cancer patients improved in the past 8 years, with reductions in both mortality and ICU LOS, suggesting improvements in overall care. However, outcomes remained poor in patients with lung cancer, requiring multiple organ support and compromised PS.
✦ ‘I think he’s dead’: A cohort study of the impact of caller declarations of death during the emergency call on bystander CPR
Référence :DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resuscitation.2021.01.001
Petit article intéressant sur les difficultés de régulation en SAMU et la perception de gravité
Résumé article :
Background In emergency calls for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA), dispatchers are instrumental in the provision of bystander cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) through the recruitment of the caller. We explored the impact of caller perception of patient viability on initial recognition of OHCA by the dispatcher, rates of bystander CPR and early patient survival outcomes.
Methods We conducted a retrospective cohort study of 422 emergency calls where OHCA was recognised by the dispatcher and resuscitation was attempted by paramedics. We used the call recordings, dispatch data, and electronic patient care records to identify caller statements that the patient was dead, initial versus delayed recognition of OHCA by the dispatcher, caller acceptance to perform CPR, provision of bystander-CPR, prehospital return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), and ROSC on arrival at the Emergency Department.
Results Initial recognition of OHCA by the dispatcher was more frequent in cases with a declaration of death by the caller than in cases without (92%, 73/79 vs. 66%, 227/343, p < 0.001). Callers who expressed such a view (19% of cases) were more likely to decline CPR (38% vs. 10%, adjusted odds ratio 4.59, 95% confidence interval 2.49–8.52, p < 0.001). Yet, 15% (12/79) of patients described as non-viable by callers achieved ROSC.
Conclusion Caller statements that the patient is dead are helpful for dispatchers to recognise OHCA early, but potentially detrimental when recruiting the caller to perform CPR. There is an opportunity to improve the rate of bystander-CPR and patient outcomes if dispatchers are attentive to caller statements about viability.
✦ Combination of delirium and coma predicts psychiatric symptoms at twelve months in critically ill patients: A longitudinal cohort study
Référence : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.01.007
Un article sur le devenir à long terme de nos chers patients de réanimation délirants…
Résumé article :
Purpose We aimed to determine any associations between delirium and comas during intensive care unit (ICU) stay, and long-term psychiatric symptoms and disability affecting activity of daily living (ADL).
Materials and methods In this prospective observational study, we enrolled critically ill adult patients that were emergently admitted to an ICU. We assessed psychiatric symptoms and disability affecting ADL at three and twelve months after ICU discharge.
Results Among the 81 and the 47 patients that responded to the questionnaires at three and twelve months, 22 (27%) and 13 (28%) patients experienced delirium, respectively. During their ICU stay, 28 (35%) and 21 (45%) had been in comas, respectively. At three and twelve months, 51 (63%) and 23 (49%) of patients experienced composite psychiatric symptoms or disability affecting ADL, respectively. After adjusting predefined confounders, the combination of delirium and comas was an independent risk factor for the presence of composite psychiatric symptoms or disability affecting ADL (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 3.38; 1.10–10.38 at three months; aOR 8.28; 1.48–46.46 at twelve months).
Conclusions In critically ill adults, combination of delirium and comas during ICU stay is a predictor of psychiatric symptoms or ADL disability.
✦ Acidemia subtypes in critically ill patients: An international cohort study
Référence : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.02.006
Purpose To study the prevalence, characteristic, outcome, and acid-base biomarker predictors of outcome for different acidemia subtypes.
Methods We used national intensive care databases from three countries and classified acidemia subtypes as metabolic (standard base excess [SBE] < −2 mEq/L only), respiratory (PaCO2 > 42 mmHg only), and combined (both SBE < −2 mEq/L and PaCO2 > 42 mmHg) based on blood gas analysis in the first 24 h after ICU admission. To investigate acid-base predictors for hospital mortality, we applied the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve approach.
Results We screened 643,689 ICU patients (2014–2018) and detected acidemia in 57.8%. The most common subtype was metabolic (42.9%), followed by combined (30.3%) and respiratory (25.9%). Combined acidemia had a mortality of 12.7%, compared with 11% for metabolic and 5.5% for respiratory. For combined acidemia, the best predictor of hospital mortality was pH. However, for metabolic or respiratory acidemia, it was SBE or PaCO2, respectively.
Conclusions In ICU patients with acidemia, mortality differs according to subtype and is highest in the combined subtype. Best acid-base predictors of mortality also differ according to subtype with best performance for pH in combined, SBE in metabolic, and PaCO2 in respiratory acidemia.
DU CÔTÉ DES AUTRES SPÉCIALITÉS :
✦ Right Ventricular Dysfunction in Early Sepsis and Septic Shock
référence : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2020.09.274
Proposition d’analyse : Analyse rétrospective de la fonction ventriculaire droite et gauche sur 393 ETT de patients en choc septique et sepsis sévère (critères SSC avant 2016). Dans cette étude, la dysfonction ventriculaire droite isolée, basée sur la mesure du TAPSE et de la fraction de raccourcissement, était indépendamment associée à une hausse de la mortalité. Les données de la littérature vont en ce sens. Il paraît important d’insister sur les indices choisis. Le TAPSE et la FR sont-ils les indices les plus pertinents de la fonction VD ? Les auteurs n’ont pas fait de doppler tissulaire et les seuils choisis semblent être restrictifs (diagnostiquaient surtout les atteintes VD sévères). Qu’en est il des dysfonctions modérées ? Dans un papier récent d’experts, la définition de la dysfonction VD était plus physiologique : dilatation VD associée à une élévation de la PVC, sans toutefois nous donner un seuil. A titre d’information, l’article suivant proposait : VD/VG > 0,6 + PVC > 8 mmHg (https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054‐020‐03345‐z ). De manière intéressante, la mesure du « strain longitudinal » VD n’était pas associée à une différence de mortalité, bien que plus basse chez les patients décédés. A cela s’ajoute beaucoup d’autres limites sur cet article, tel que l’absence d’indication sur les pathologies causales de la dysfonction VD, niveau de PEEP utilisé, SDRA …
Il reste difficile de définir ce qu’est la dysfonction VD, offrant une grande hétérogénéité de la littérature sur la question.
Abstract :
Background Sepsis is a frequently lethal state, commonly associated with left ventricular (LV) dysfunction. Right ventricular (RV) dysfunction in sepsis is less well understood.
Research Question In septic patients, how common is RV dysfunction, and is it associated with worse outcomes?
Study Design and Methods We measured echocardiographic parameters on critically ill patients with severe sepsis or septic shock within the first 24 hours of ICU admission. We defined RV dysfunction as fractional area change (FAC) less than 35% or tricuspid annulus systolic plane excursion (TAPSE) less than 1.6 cm. We defined LV systolic dysfunction as ejection fraction (EF) less than 45% or longitudinal strain greater than -19%. Using logistic regression, we assessed the relationship between 28-day mortality and presence of RV dysfunction and LV systolic dysfunction, controlling for receipt of vasopressors, receipt of fluid, mechanical ventilation, and the acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE II) score.
Results We studied 393 patients. RV and LV dysfunction were common (48% and 63%, respectively). Mean echocardiographic values were: RV end-diastolic area, 22.4 ± 7.0 cm 2; RV end-systolic area, 14.2 ± 6.0 cm 2; RV FAC, 38 ± 11%; TAPSE, 1.8 ± .06 cm; RV longitudinal strain, -15.3 ± 6.5%; LV EF, 60% ± 14%; LV longitudinal strain, -16.5% ± 6.0%. Patients with RV dysfunction had higher 28-day mortality (31% vs 16%, P = .001). In our multivariable regression model, RV dysfunction was associated with increased mortality (OR, 3.4; CI, 1.7-6.8; P = .001), and LV systolic dysfunction was not (OR, 0.63; CI, 0.3 -1.2; P = .32)
Interpretation Right ventricular dysfunction is present in nearly half of studied septic patients and is associated with over threefold higher 28-day mortality.
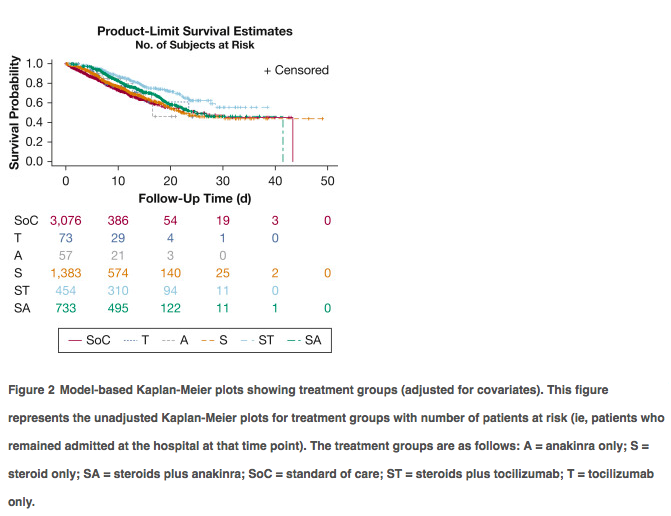
✦ Comparative Survival Analysis of Immunomodulatory Therapy for Coronavirus Disease 2019 Cytokine Storm
Référence : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chest.2020.09.275
Commentaire: Une autre analyse rétrospective avec un gros effectif (après RECOVERY et REMAP CAP) soutenant l’intérêt d’une association d’un anti IL-6 et corticoides plutôt que corticoides seuls avec impact sur la mortalité, après ajustement. Ici, il ne s’agit pas que de patients de réanimation et il n’existe pas d’analyse en sous groupe des patients les plus sévères. Il s’agit d’une étude rétrospective comprenant des centres généraux et universitaires, les modalités d’admission du tocilizumab et des corticoides ne sont pas connus en dehors de leur délai d’instauration. L’administration de corticoides était plus précoce (27,6h) que le tocilizumab (54,4h après admission). Le délai d’administration du toci seul était similaire. On pourrait s’imaginer que la co-administration plus précoce du toci pourrait être encore plus bénéfique et ce, chez les patients les plus graves.
Abstract :
Background Cytokine storm is a marker of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) illness severity and increased mortality. Immunomodulatory treatments have been repurposed to improve mortality outcomes.
Research question Do immunomodulatory therapies improve survival in patients with COVID-19 cytokine storm (CCS)?
Study design and method We conducted a retrospective analysis of electronic health records across the Northwell Health system. COVID-19 patients hospitalized between March 1, 2020, and April 24, 2020, were included. CCS was defined by inflammatory markers: ferritin, > 700 ng/mL; C-reactive protein (CRP), > 30 mg/dL; or lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), > 300 U/L. Patients were subdivided into six groups: no immunomodulatory treatment (standard of care) and five groups that received either corticosteroids, anti-IL-6 antibody (tocilizumab), or anti-IL-1 therapy (ana- kinra) alone or in combination with corticosteroids. The primary outcome was hospital mortality.
Results Five thousand seven hundred seventy-six patients met the inclusion criteria. The most common comorbidities were hypertension (44%-59%), diabetes (32%-46%), and cardiovascular disease (5%-14%). Patients most frequently met criteria with high LDH (76.2%) alone or in combination, followed by ferritin (63.2%) and CRP (8.4%). More than 80% of patients showed an elevated D-dimer. Patients treated with corticosteroids and tocilizumab combination showed lower mortality compared with patients receiving standard-of-care (SoC) treatment (hazard ratio [HR], 0.44; 95% CI, 0.35-0.55; P < .0001) and with patients treated with corticosteroids alone (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.53-0.83; P 1⁄4 .004) or in combination with anakinra (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.50-0.81; P 1⁄4 .003). Corticosteroids when administered alone (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.57-0.76; P < .0001) or in combination with tocilizumab (HR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.35-0.55; P < .0001) or anakinra (HR, 0.68; 95% CI, 0.57-0.81; P < .0001) improved hospital survival compared with SoC treatment.
Interpretation The combination of corticosteroids with tocilizumab showed superior survival outcome when compared with SoC treatment as well as treatment with corticoste- roids alone or in combination with anakinra. Furthermore, corticosteroid use either alone or in combination with tocilizumab or anakinra was associated with reduced hospital mortality for patients with CCS compared with patients receiving SoC treatment.
Rappels :





 25 mars 2021
25 mars 2021